Network Segmentation, Vlans, & Subnetting
Implementing segmentation, VLAN assignments, and subnetting optimizes traffic flow and meets the healthcare office’s security and compliance needs.
Overview
As we transition from a basic SoHo setup to an enterprise-grade network, Network Segmentation is a core pillar of our security and performance strategy. By splitting our infrastructure into multiple logical segments (VLANs), we reduce the attack surface, better contain threats, and tailor resource access based on department or device type. This ensures that sensitive data such as Patient Health Information (PHI) remains isolated from general office traffic and public-facing services.
- Enforces Zero-Trust principles by limiting default trust between subnets.
- Simplifies Access Control with refined ACLs and firewall rules.
- Enables Scalability and modular growth, accommodating new services and devices with ease.
Why Subnetting Matters
Subnetting divides a larger IP address space into smaller, logical networks. In an enterprise healthcare environment, this is essential for effective management of IP ranges, clear separation of devices, and minimizing broadcast traffic. Our approach leverages both IPv4 and IPv6 planning to ensure long-term compatibility and easy growth.
Subnetting Theory
Breaking a Class A/B/C network into smaller subnets can drastically reduce congestion on broadcast domains. This fosters improved performance and clarity on large-scale networks.
CIDR Benefits
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) enables flexible subnet masks, avoiding IP wastage and providing finer control over how addresses are allocated.
Routing Efficiency
With clearly defined subnets, routing policies become more efficient, allowing us to implement advanced ACLs and next-gen firewalls with fewer ambiguities.
VLAN Architecture & Design
Our deployment utilizes Cisco Catalyst switches and RADIUS-based authentication to dynamically assign VLANs to user endpoints. Each VLAN is crafted around departmental or data sensitivity requirements:
| VLAN ID | Department | IP Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Administration | 192.168.10.0/24 | Office Management, HR |
| 20 | Medical Staff | 192.168.20.0/24 | PHI Access, EHR Systems |
| 30 | Guest Wi-Fi | 192.168.30.0/24 | Isolated Internet Access |
| 40 | VoIP | 192.168.40.0/24 | Phone System & IP Handsets |
| 50 | Servers & DB | 192.168.50.0/24 | On-Prem Database & Active Directory |
- Medical Staff VLAN is behind advanced ACLs & IDS/IPS for PHI protection.
- Guest VLAN ensures visitors have Internet-only access with no internal resource visibility.
- Server VLAN restricts traffic to the database and domain controllers, allowing secure backups and minimal lateral movement.
Security & Access Controls
VLAN segmentation is only as robust as the policies and rules that govern inter-VLAN traffic. For this healthcare network, we integrate VLANs with a layered Access Control approach:
ACL Policies
Each VLAN-to-VLAN communication path is explicitly defined in our firewall or layer-3 switch ACL. By default, Deny All is enforced, requiring administrators to whitelist only essential traffic.
RADIUS Authentication
User and device credentials pass through a RADIUS server, ensuring only authenticated entities can join VLANs. This merges well with our Zero-Trust Architecture.
IPS/IDS Integration
Intrusion Prevention/Detection Systems are placed at key network junctions, scanning real-time traffic for anomalies or malicious activity. Suspicious packets are blocked or quarantined automatically.
Policy Audits
Routine HIPAA compliance checks confirm that ACLs, logs, and network flow data match regulatory standards for data security and privacy.
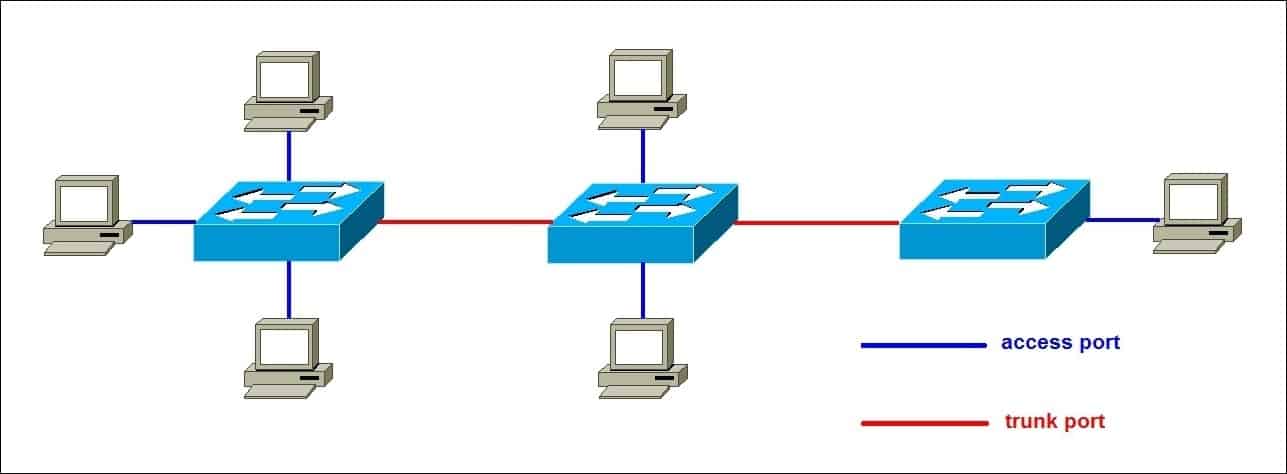
Trunking & Inter-VLAN Routing
Our Cisco Catalyst Switches use 802.1Q trunking to forward multiple VLANs through a single physical link. At the core layer, a Layer-3 switch or firewall handles inter-VLAN routing:
- Trunk Ports connect distribution switches and provide the VLAN tags needed for traffic segregation.
- Native VLAN is set to a non-default ID to avoid security risks associated with VLAN1.
- ROAS (Router-on-a-Stick) or routed interfaces on the core switch manage traffic flow between subnets.
Diagram Placeholder: 802.1Q Trunking Example
Sample Subnet Allocation
Below is a simplified IP plan reflecting how we allocate addresses for each VLAN. This includes DHCP scopes on our Windows Server and static reservations for critical devices like firewalls, servers, and VoIP controllers.
Dynamic leases are set for end-user devices, while static addresses are reserved for our PA220 Firewall, Cisco Switches, and Windows Domain Controllers. This structure ensures that critical infrastructure IPs never change, aiding in both stability and security auditing.
Monitoring & Compliance Checks
Maintaining strong segmentation is an ongoing process. With the installed Spiceworks Inventory and Cisco Security Suite, we keep an eye on VLAN traffic patterns, looking for anomalies that might indicate unauthorized access or policy drift.
Real-Time Traffic Analysis
Network flow data is visualized in dashboards, highlighting VLAN utilization and potential bottlenecks.
Unauthorized Access Alerts
If a device appears in a VLAN it’s not authorized for, automated alerts prompt immediate investigation.
HIPAA Audit Trails
All VLAN policy changes and user actions are logged, facilitating compliance reviews and regulatory checks.
Conclusion & Next Steps
By meticulously planning subnets, designing VLANs, and enforcing strict access controls, this healthcare network is now positioned for enterprise-level security and performance. With RADIUS-based authentication, advanced IPS/IDS monitoring, and robust VLAN trunking, we minimize the risk of data breaches and maintain HIPAA compliance. The next phase is to integrate our segmented environment into a VoIP configuration strategy, ensuring seamless communication and operational efficiency.
